Map Plugin using Kepler.gl
Kepler.gl is a powerful tool for creating beautiful maps. With this plugin, your AI assistant can help you and your customers to create a map from your own data by just prompting the AI assistant.
For example, suppose you have a dataset that contains the location, revenue and customer population. Within your application, you may have a function to call a data API to get this data:
const getRevenueData = async () => {
const response = await fetch('https://your-data-api.com/revenue');
return response.json();
};
The json data could look like this:
const myDatasets = {
myVenues: [
{ "location": "New York", latitude: 40.7128, longitude: -74.0060, revenue: 100000, population: 8000000 },
{ "location": "Los Angeles", latitude: 34.0522, longitude: -118.2437, revenue: 150000, population: 4000000 },
{ "location": "Chicago", latitude: 41.8781, longitude: -87.6298, revenue: 120000, population: 2700000 }
]
};
You can use the AI assistant to create a map from this data by just asking the AI assistant:
Can you create a map using the data myVenues?
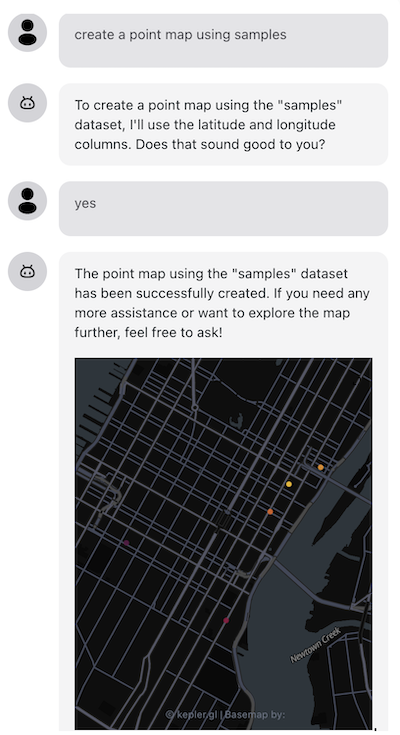
Let's see how to wire this up in your application
Step 1: Setup the OpenAssistant in your application
Install the OpenAssistant package in your application.
yarn add @openassistant/core @openassistant/keplergl @openassistant/ui
For @openassistant/keplergl, you need to install the kepler.gl package in your application.
yarn add @kepler.gl/actions @kepler.gl/components @kepler.gl/constants @kepler.gl/layers @kepler.gl/reducers @kepler.gl/styles @kepler.gl/utils @kepler.gl/processors @kepler.gl/localization
import { AiAssistant } from '@openassistant/ui';
// only for React app without tailwindcss
import '@openassistant/ui/dist/index.css';
const assistantProps = {
name: 'My AI Assistant',
description: 'This is my AI assistant',
version: '1.0.0',
modelProvider: 'openai',
model: 'gpt-4',
apiKey: 'your-api-key',
welcomeMessage: 'Hi, I am your AI assistant',
instructions:
"You are a data and map analyst. You can help users to create a map from a dataset. If a function calling can be used to answer the user's question, please always confirm the function calling and its arguments with the user.",
functions: [],
};
The instructions is the most important part of the assistant. It will be used to guide the AI assistant to work within the context of your application e.g. what questions can be answered by the AI assistant.
Step 2: Share the meta data of your dataset with the AI assistant
Share the meta data of your dataset, so the assistant can understand which datasets are available to use when creating a map.
The meta data is good enough for the AI Assistant. Don't put the entire dataset in the context, and there is no need to share your dataset with the AI Assistant or the LLM models. The LLM models will only need the meta data of your dataset to create a map.
const dataContext = useMemo(() => {
// Note: you can call your data API to get the meta data of your dataset
return [
{
description: 'Please use the following meta data for function callings.',
metaData: [
{
datasetName: 'myVenues',
fields: ['name', 'longitude', 'latitude', 'revenue', 'population'],
},
],
},
];
}, []);
// you can simply append the context to the `instructions` of the assistant props
assistantProps.instructions =
assistantProps.instructions + '\n' + JSON.stringify(dataContext);
To get up to date with your data context, e.g. when dataset been added or removed, you can use the useAssistant hook to add the context to the assistant props.
import {useAssistant} from '@openassistant/core';
const { initializeAssistant, addAdditionalContext } =
useAssistant(assistantProps);
// initialize assistant with context
const initializeAssistantWithContext = async () => {
await initializeAssistant();
addAdditionalContext({ context: JSON.stringify(dataContext) });
};
useEffect(() => {
// Note: when your dataContext is updated, this will trigger the assistant to update the context
initializeAssistantWithContext();
}, [dataContext, addAdditionalContext]);
Step 3: Import the predefined mapping function calling
Import the predefined mapping callback function from the keplergl plugin and add it to the assistant.
import { createMapFunctionDefinition, GetDatasetForCreateMapFunctionArgs } from '@openassistant/keplergl';
const myFunctions = [
createMapFunctionDefinition({
getDataset: ({datasetName}: GetDatasetForCreateMapFunctionArgs) => {
// check if the dataset exists
if (!myDatasets[datasetName]) {
throw new Error('The dataset does not exist.');
}
return myDatasets[datasetName];
},
})
];
Step 4: Replace the functions inthe assistant props and render the AI Assistant component
// update the functions in the assistant props
const assistantProps = {
name: 'My AI Assistant',
description: 'This is my AI assistant',
version: '1.0.0',
modelProvider: 'openai',
model: 'gpt-4',
apiKey: 'your-api-key',
welcomeMessage: 'Hi, I am your AI assistant',
instructions:
"You are a data and map analyst. You can help users to create a map from a dataset. If a function calling can be used to answer the user's question, please always confirm the function calling and its arguments with the user.",
functions: myFunctions,
};
return <AiAssistant {...assistantProps} />;
Now you can start the conversation with the AI assistant and ask it to create a map from your dataset.
Can you create a map using the data myVenues?
If you prompt with the wrong dataset name, the AI assistant will return an error message.
Can you create a map using the data myPeronalTrip?
If your dataset doesn't contain any geometry data, the AI assistant will response with an error message.
Advanced: more configurations of the mapping function
Coming soon.